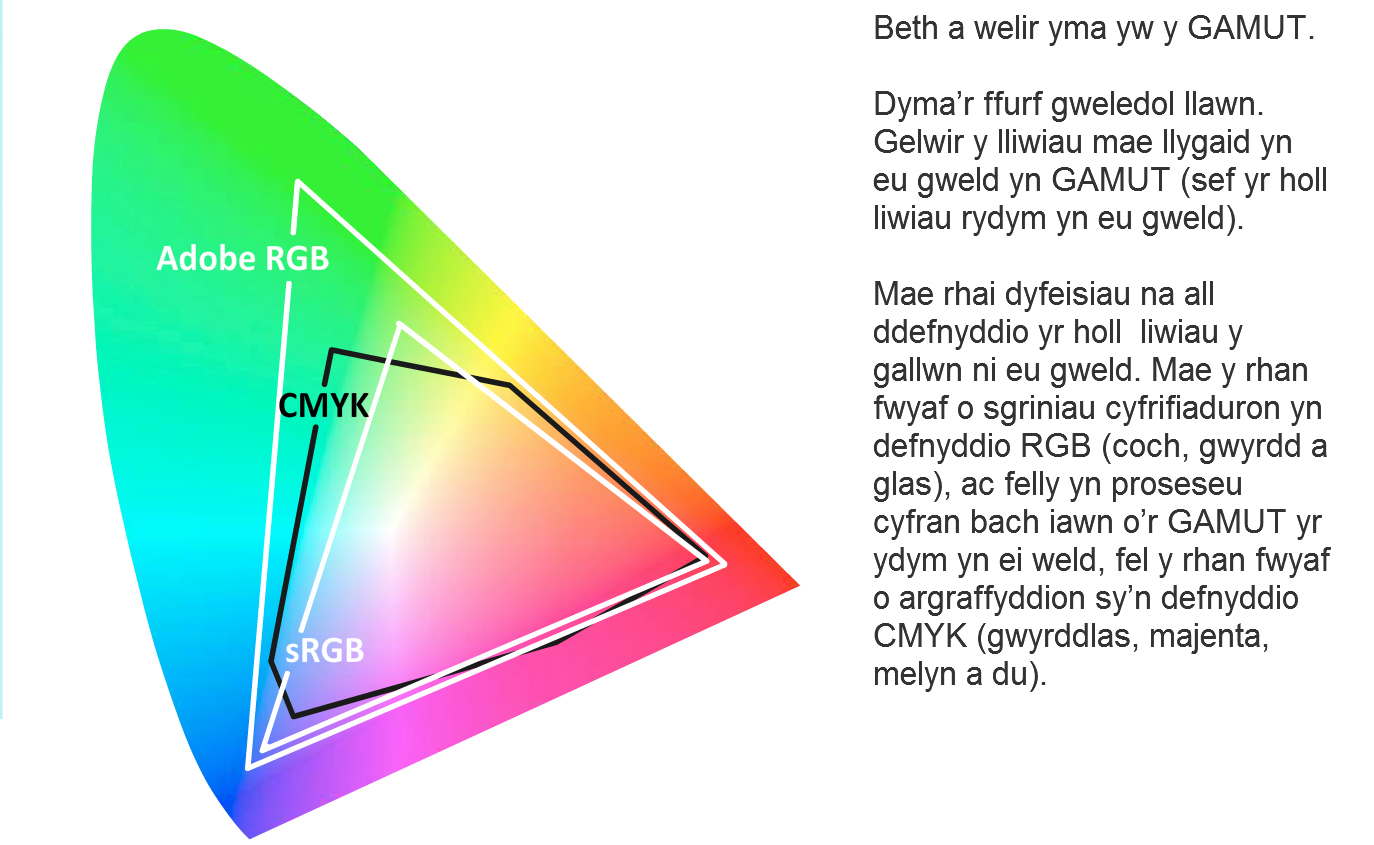
Lliw Gamwt, dosbarthiadau a phriodweddau
Colour Gamut, Categories & properties
Lliw
Daw lliw o sbectrwm golau, oherwydd ei fod yn cael ei adlewyrchu neu ei amsugno.
Gamwt
Gamwt yw’r lliwiau mae’r llygaid dynol yn eu codi (yr holl liwiau y gallwch chi eu gweld).
Prosesau
Mae rhai dyfeisiau methu defnyddio’r holl liwiau a welwn. Mae’r rhan fwyaf o sgriniau cyfrifiadurol yn defnyddio RGB (coch, gwyrdd a glas) felly dim ond ychydig o’r gamwt a welwn maent yn eu prosesu. Mae’r rhan fwyaf o argraffwyr yn defnyddio CMYK (gwyrddlas, magenta, melyn a du).
Lliwiau Oer a Phoeth
Gellir dosbarthu lliwiau yn rhai Poeth ac Oer. Mae coch neu felyn mewn lliwiau poeth, a glas mewn lliwiau oer. Nid yw du a gwyn yn oer nac yn boeth. Dywedir bod lliwiau oer yn atchwelyd [regress] (lliwiau trist) ond mae lliwiau poeth yn lliwiau prosesu (lliwiau hapus, calonogol).
| Poeth | Oer |
|---|---|
| Coch | Glas |
| Melyn | Gwyrddlas |
| Oren | Gwyrdd y môr |
| Gwyrddfelyn | Fioled |
| Rhuddgoch | Llwyd |
Prosesau
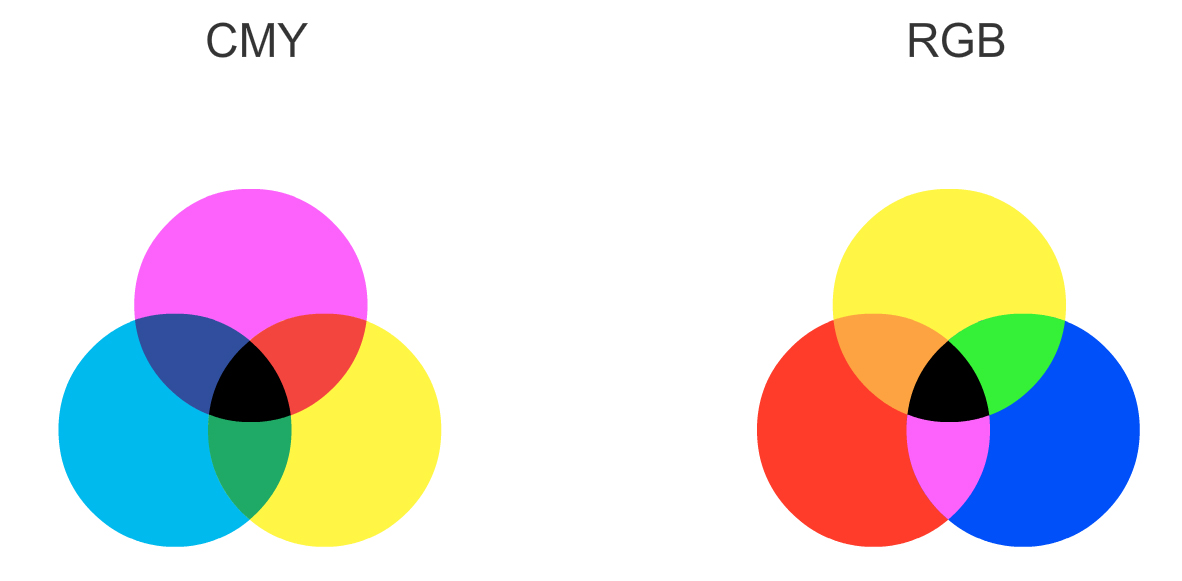
Gellir cymysgu lliwiau i gynhyrchu lliw ychwanegol (additive) a thynnol (subtractive).
Dyma’r ffordd mae lliw yn cael ei gynhyrchu ar gyfer monitor, teledu, taflunydd, sganiwr ac unrhyw beth arall sy’n defnyddio golau tri lliw (RGB - Coch, gwyrdd, glas).

Dyma’r ffordd y caiff lliw ei gynhyrchu pan fydd golau yn adlewyrchu oddi ar y gwrthrych. Dyma pryd fydd arwyneb yn cael ei liwio fel sy’n digwydd yn y broses argraffu neu mewn unrhyw fath o beintio.
Priodweddau Lliwiau
Gall lliwiau amrywio drwy newid y priodweddau canlynol. Dirlawnder, disgleirdeb, tymheredd, arlliw, tint a thôn.
Colour
Colour comes from a spectrum of light, as it is reflected or absorbed.
Gamut
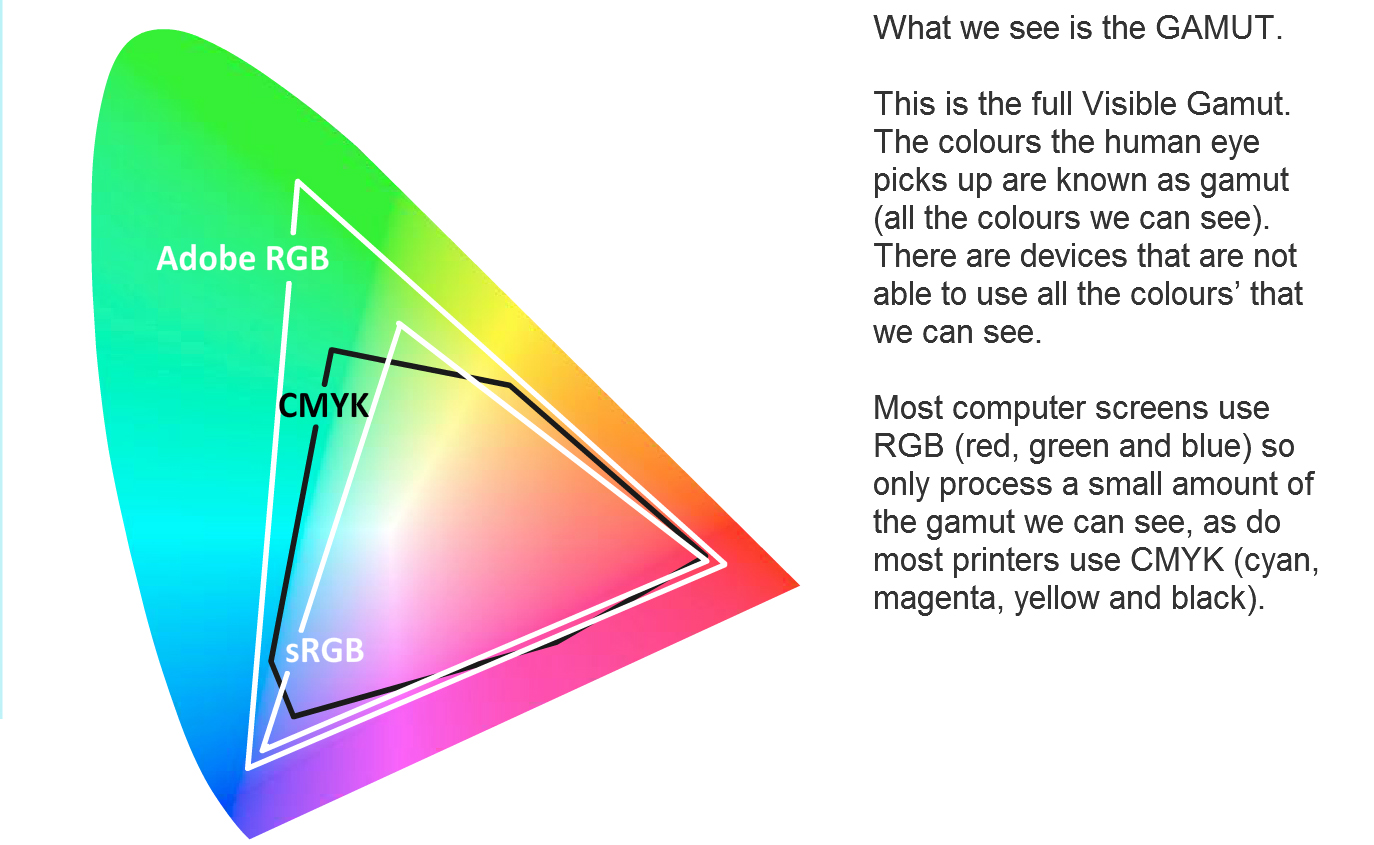
The colour the human eye picks up are known as gamut (all the colours we can see)
Process
There are devices that are not able to use all the colours’ that we can see. Most computer screens use RGB (red, green and blue) so only process a small amount of the gamut we can see, as do most printers use CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow and black).
Hot & Cold Colours
Colours can be categorised as Hot & Cold colours. Hot colours contain red or yellow where as cold colours would contain blue. Black and white, are neither hot nor cold. Cold colours are said to regress (to be sad, gloomy colours) where as hot colours have the opposite effect being process colours (happy, cheery optimistic colours).
| Hot | Cold |
|---|---|
| Red | Blue |
| Yellow | Turquoise |
| Orange | Sea Green |
| Yellowish green | Violet |
| Crimson | Grey |
Colour Mixing Systems
Colours can be mixed to produce additive and subtractive mixes.
This is the way that colour is produced for Monitors, TV's, Projectors, Scanners and anything else that uses three colour (RGB) light.

This is the way that colour is produced when light is reflected from the object. That is when a surface is coloured as in printing or any form of painting.

Colour Properties
Colours can vary by changing the following properties, saturation, brightness, temperature, hue, tint & tone.